BLEASS Monolit combines the rich analogue sound and intuitive ease-of-use of BLEASS Alpha with the creative expressiveness of BLEASS Omega. The result is a compact, efficient, mono-synth tailor-made for creating thunderous basses, searing leads, sparkling arpeggios and other-worldly SFX.
And it’s completely free!
Just download to your desktop, iPhone or iPad, and immediately start designing and playing original and inspirational sounds. And thanks to Monolit’s super-efficient low-CPU synth engine, even the humblest of devices will have no problem running many instances of this fabulous-sounding synth.
The instrument’s interface is super-straightforward and easy to use, with intuitive graphic controls and long-throw faders that feel tactile and precise whether you are using touch screen or mouse. If you need some extra sonic inspiration, BLEASS Monolit includes a dice button that generates new values for all the synth’s settings, but does so in a way that’s carefully tuned to create useable yet unique sounds. And of course, as with all BLEASS products, Monolit comes with a library of factory presets packed with a wide variety of different sounds, with additional sound packs also available produced by BLEASS’ network of talented sound designers.

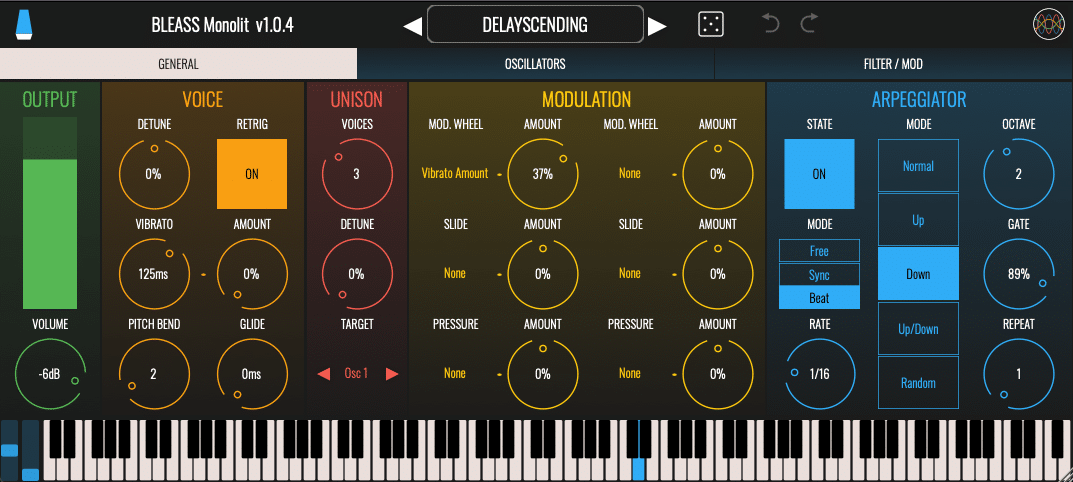
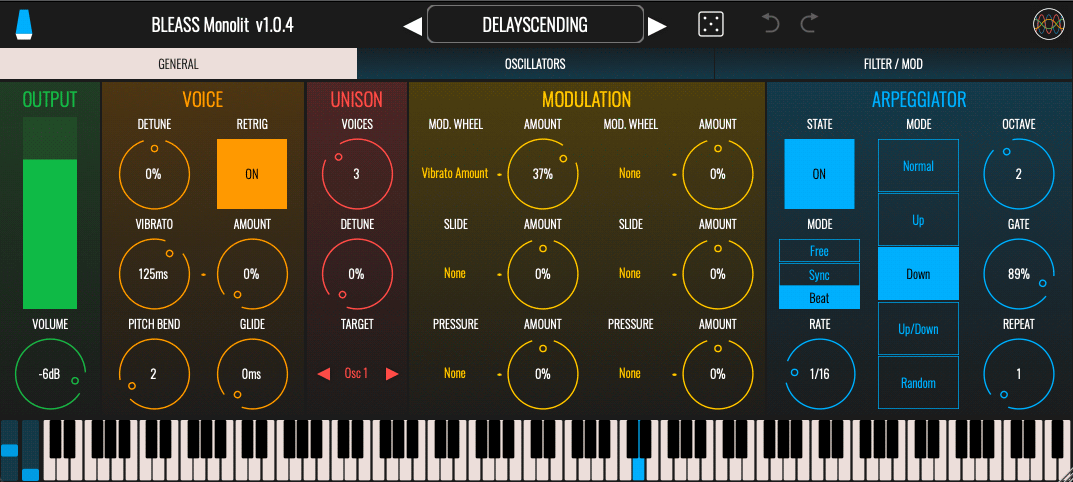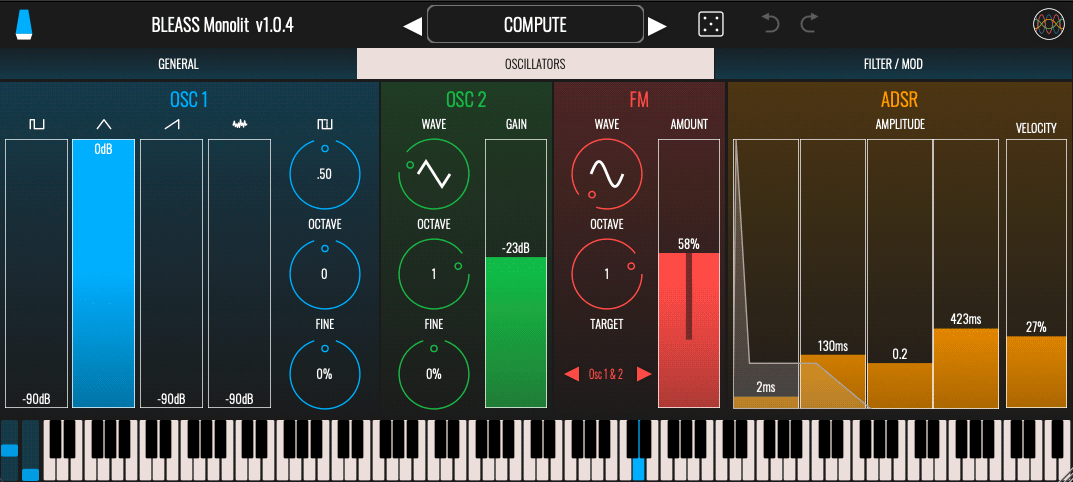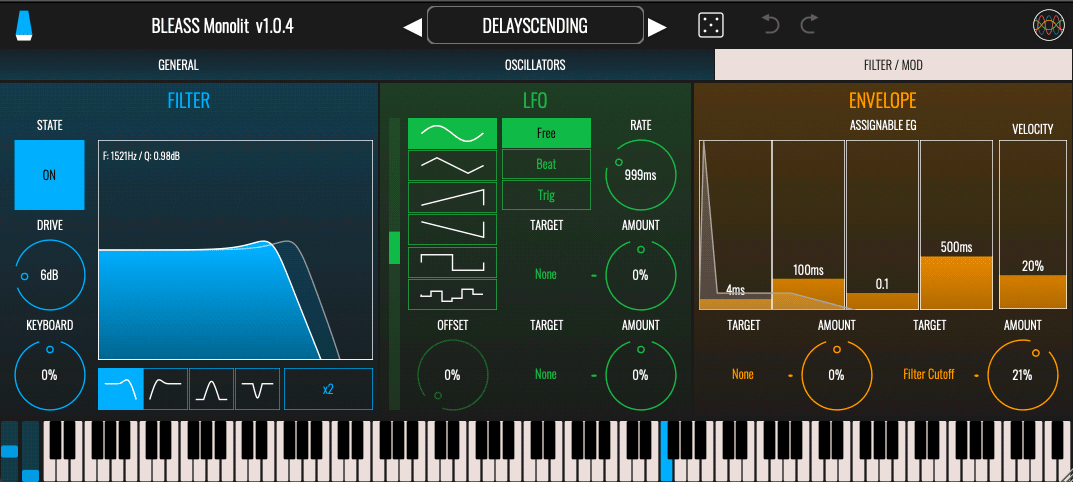
GENERAL TAB
OUTPUT – Controls and visualises the instrument’s output level.
Volume: Sets the desired output level
Meter: Visualises the current peak output level of the instrument
VOICE – Provides access to basic voicing parameters
Detune: Sets a master detuning that affects the entire synth, in the range ±0.5 semitones.
Retrig: Enables or disables the retriggering of ADSR envelopes when playing legato
Vibrato: Sets the rate, in milliseconds, of the global pitch vibrato
Amount: Sets the strength of the global pitch vibrato. A setting of 100% means the global tuning will oscillate between -1 semitone and +1 semitone.
Pitch Bend: Determines the maximum pitch bend range, in semitones.
Glide: Sets the time taken for the synth’s pitch to ramp from the last-played note to the currently-played note.
UNISON – BLEASS Monolit includes a Unison algorithm that creates up-to seven duplicates of synth’s voice. With detuning applied, this creates a thicker, fuller sound.
Voices: Sets the number of voice duplicates to create, from 0 to 7.
Detune: Sets the amount of detuning to apply to the unison voices. The detuning is spread amongst the voices, with a setting of 100% meaning that the most-detuned voice(s) will be 1 semitone above and/or below the played note.
Target: Choose whether to apply the unison algorithm to both oscillators, or only one or other of them.
MODULATION – Route incoming Mod Wheel, Slide and Pressure messages to Monolit’s parameters. Each controller source can be routed to two destinations.
Mod. Wheel: Responds to standard MIDI modulation wheel messages (MIDI CC 1)
Slide: Responds to note-specific CC-74 messages received from MPE-compatible controllers. In BLEASS Monolit, Slide’s behaviour is set to relative.
Pressure: Responds to MIDI Aftertouch messages, produced by changing the pressure being applied to the key of a compatible keyboard or controller.
Destination Selection Menus: Use the destination selection menus listed under each modulation source name to choose the synth parameter that should receive the controller messages.
Amount Dials: Scales the strength of the controller message being routed to a synth parameter.
ARP – Configure the built-in arpeggiator
State: Enables or disables the arpeggiator
Mode: Sets the sync mode of the arpeggiator.
- FREE uses an internal timer that is set within the instrument.
- SYNC synchronises the arpeggiator to the host DAW’s beat.
- BEAT synchronises the arpeggiator to the host DAWs beat and synchronises the arpeggiator’s pattern position to the host’s bar-and-beat location.
Rate: Sets the speed of the arpeggiator.
- In FREE mode, the rate is set in milliseconds
- In SYNC and BEAT modes, the rate is a factor of the host DAW’s beat length.
Mode: Determines the pattern of notes that the arpeggiator will produce.
- NORMAL: Notes are played in the order in which they were triggered.
- UP: Notes are played in pitch order, from lowest to highest.
- DOWN: Notes are played in pitch order, from highest to lowest.
- UP/DOWN: Notes are played in succession, from lowest to highest, and then back to lowest.
- RANDOM: Notes are played in a random order
Octave: Sets the number of additional octaves that the arpeggiator should cover. When set to “0”, only the triggered notes will be played. When set to “1”, notes that are one octave higher than the triggered notes are added to the arpeggio; higher settings add further octaves.
Gate: Sets the duration of the arpeggiator’s notes, as a proportion of the arpeggiator’s rate setting.
Repeat: Sets the number of times each note is repeated before the arpeggiator moves on to the next note.

OSCILLATORS TAB
OSC 1 – Monolit’s first oscillator can produce a blend of four different waveforms: Pulse, triangle, sawtooth and noise.
Waveform Volume Faders: The faders set the volume of each of the waveforms produced by the oscillator.
Pulse Width: Sets the pulse width of the pulse waveform. A setting of 0.5 produces a square wave; higher and lower settings produce an increasingly narrow pulse.
Octave: Determines the octave offset of the oscillator.
Fine: Adjusts the oscillator’s fine tuning. The value is shown as a percentage of a semitone.
OSC 2 – The second oscillator produces a single, selectable waveform.
Wave: Selects the waveform that the oscillator will produce. The waveform can be morphed smoothly from sine wave, through triangle and sawtooth waves, to square wave.
Octave: Determines the octave offset of the oscillator.
Fine: Adjusts the oscillator’s fine tuning. The value is shown as a percentage of a semitone.
Gain: Sets the output volume level of the oscillator.
FM – Monolit includes an FM stage that can modulate the frequency or one, other, or both oscillators. Expressed in terms of FM synthesis, Monolit’s FM operator acts as a modulator, whilst the instrument’s analogue-style oscillators act as carriers.
Wave: Choose the FM waveform that will be applied to the target oscillator(s). The waveform can be morphed smoothly from sine wave, through triangle and sawtooth waves, to square wave.
Octave: Applies an octave offset to the FM operator’s frequency.
Target: Determines which of the analogue oscillators will be modulated by the FM operator.
Amount: Sets the strength of the FM effect.
ADSR – Configures the instrument’s amp envelope.
ADSR Faders: The envelope faders allow you to set the envelope’s attack time, decay time, sustain level and release time (respectively) in a visually intuitive manner. The resulting envelope shape is shown overlaying the faders.
Velocity: Determines how strongly playing velocity affects the amplitude of the note that’s produced.